Table of Contents
These products & services are researched and tested by HelpGuide’s independent consumer reviews partner. When you buy through the links, we earn a commission.
Fewer than one in five people with hearing loss in the United States use hearing aids. Many people delay hearing loss treatment for an average of 10 years, with the expense being the main reason. Unfortunately, people with untreated hearing loss are more likely to experience a lower quality of life due to depression, anxiety, social isolation, cognitive decline, poor balance—even decreased income. The solution is simple yet unaffordable for many since hearing aids cost an average of more than $3,000 per pair, with some brands charging more than $7,000.
Fortunately, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the sale of over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids in October 2022. This allowed hearing aid manufacturers to develop devices that don’t need to be fitted or adjusted by an audiologist, resulting in more affordable hearing aids that you can purchase online or in-store without a prescription.
There is very minimal evidence to support that a top-of-the-line hearing aid will result in significantly better speech understanding over a basic or mid-level product. In my professional opinion, there is really no reason to go with a top-of-the-line device for the situations and concerns the majority of people express.
Gina Angley, an audiologist and owner of the Tennessee-based Nashville’s Hearing & Communication Center
Today, OTC hearing aids are available for less than $2,000 per pair, and our tests show that hearing aids in the $300–$500 range can offer good sound quality and premium features, like rechargeable batteries and Bluetooth streaming. Our testers noticed that hearing aids below $300 start to have lower sound quality, difficult adjustments, and glitchy controls.
We want you to find a hearing aid that’s not only affordable but also works well, so our recommendations balance performance with price. We also share tips for saving money on hearing aids at any price, how to check your insurance coverage, and who to contact for free hearing aids.
Which affordable hearing aid is right for you?
- Best overall: Jabra Enhance
- Most user-friendly app: Lexie Hearing
- Best for lifetime audiology support: MDHearing
- Best for Bluetooth streaming: Go Hearing
Why HelpGuide cares about hearing loss



Hearing and mental health are closely related. In fact, people with hearing loss tend to experience higher rates of anxiety, depression, and social isolation, which can result in loneliness and frustration, according to research.
Hearing loss is also a risk factor for developing dementia, with recent research showing how using hearing aids can slow cognitive decline in older adults and reduce the risk of dementia.
The impact of hearing loss on physical and mental health is far-reaching. This is why at HelpGuide, we’ve made it our mission to give every person access to the best information about hearing aids, so we can also help get quality products into the hands of people who need them.
There is no doubt that using hearing aids can significantly improve mental health for those with hearing loss. Addressing hearing loss early can prevent or minimize its negative impact on mental health.
Peter Byrom, an audiologist and owner of Sheffield, England-based Peter Byrom Audiology
Our Handbook Team hand-tests every hearing aid brand we review, so we can feel confident recommending the best products for our readers. We consult with audiologists, researchers, and industry leaders in hearing health, as well as mental health experts, to vet our choices and help us better understand the nuances of how hearing health impacts physical and mental health.
We also put ourselves in the consumer’s shoes by mystery shopping brands and walking through the set-up process, just like new customers. Additionally, we interview real people with hearing loss and survey hearing aid users.
By compiling our testing data, interview and survey results, and insights from hearing care providers, we formulate a strongly informed perspective that we’re sharing with you here.
Learn more about our hearing aids review methodology.
What you need to know about the best affordable hearing aids
Our testing experience
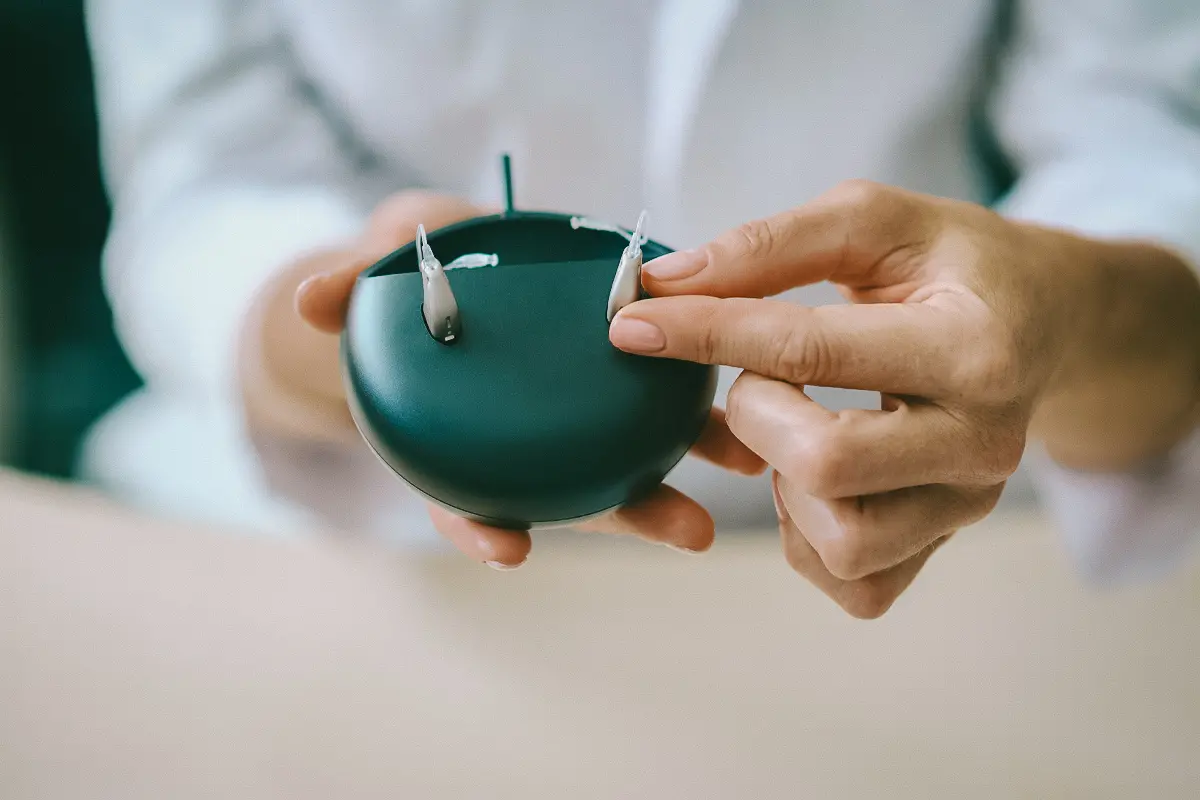
The Handbook Team has tested more than 30 hearing aids that cost between $99–$4,598 per pair.
During our tests, we go through the complete buying process as mystery shoppers, set up the hearing aids according to the user manual or app instructions, wear the hearing aids to assess comfort, test all features, and perform routine maintenance.
Our detailed, standardized approach allows us to compare hearing devices easily in nuanced ways, like determining which charging cases are the simplest to use thanks to strong magnetic ports and clear status lights. As such, our testing experiences form the crux of our reviews.
When selecting the most affordable hearing aids, we first settled on a price limit of $2,000. To many people, this is hardly affordable, yet it’s a fraction of the cost of the most expensive hearing aids on the market. With this upper limit, we could confidently recommend some of the best OTC hearing aids while also highlighting worthy options as low as $297 per pair.
Most hearing aids we tested that cost below $300 failed to meet our testing standards. Therefore, our list doesn’t represent the most affordable hearing aids for sale. Instead, we chose the most affordable devices that are also good quality.
From our tester
“The Go Ultra and Go Prime from Go Hearing are good choices to help you get started with hearing aids. They’re budget-friendly and compact devices that are easy to use. Overall, they’re a good product for the cost.”
Compare the best inexpensive hearing aids
| Brand | Price per pair | Type of hearing aid | Degree of hearing loss | Battery type | Learn More |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $799–$1,995 | In-the-ear (ITE), Receiver-in-canal (RIC) | Mild to moderate | Rechargeable, disposable | Visit Site | |
| $799–$999 | Behind-the-ear (BTE), RIC | Mild to moderate | Rechargeable, disposable | Visit Site | |
| $297–$699 | BTE, In-the-canal (ITC) | Mild to moderate | Rechargeable | Visit Site | |
| $169–$499 | ITE, BTE | Mild to moderate | Rechargeable | Visit Site |
The best affordable hearing aids reviews
1. Jabra Enhance: Best overall
2. Lexie Hearing: Most user-friendly app
3. MDHearing: Best for lifetime audiology support
4. Go Hearing: Best for Bluetooth streaming
Things to consider about affordable hearing aids
Hearing aids under $2,000 are less likely to have convenient features like Bluetooth streaming and automatic mode switching, low-profile designs, colors that match multiple skin tones, and technology that reduces background noise to an award-winning level. But none of that means affordable hearing aids can’t help you hear better. As long as you have mild to moderate hearing loss, affordable OTC hearing aids can work for you.
If there’s some wiggle room in your budget, you may not be sure whether you should spend more than $2,000 on hearing aids. Here are the main advantages and disadvantages to buying budget hearing aids:
What we like:
- No hearing test required.
- Online and in-store buying options.
- Bluetooth streaming options.
- App connectivity options.
- Rechargeable and disposable batteries are available.
- Behind-the-ear and in-the-ear styles are common.
What we don’t like:
- Usually come in one color.
- Tend to have a shorter rechargeable battery life than more expensive hearing aids.
- Can’t treat more severe levels of hearing loss.
- Less likely to have a telecoil or be compatible with hearing assistive devices.
How much do hearing aids cost?

Hearing aids cost anywhere from $99–$7,000 per pair. This extraordinary range represents both OTC and prescription hearing aids with considerable differences in technology and audiology support.
OTC hearing aids are usually the more affordable option, averaging about $1,600 per pair. Prescription hearing aids cost an average of $4,600, with the most affordable options retailing for less than $2,000 per pair. Compare and contrast both types in our review of the overall best hearing aids.
If someone is paying more than $6,000 for a top-of-the-line device with bundled services, I would say they are being taken advantage of and should not purchase. There is no reason for devices to be that expensive, and this leads to the perception that hearing aids are too expensive.
Gina Angley, audiologist and owner of the Tennessee-based Nashville's Hearing & Communication Center
Why are hearing aids so expensive?
OTC hearing aid prices reflect the following:
- Money spent researching and developing features and technology.
- Price of materials, such as rechargeable batteries, water-resistant coatings, and Bluetooth chips.
- Cost of employing audiologists and hearing instrument specialists for customer support.
Prescription hearing aid prices reflect the device's cost and the audiologist’s follow-up care. According to Angley, hearing care professionals can buy hearing aids for $200–$1,400. They’re then sold to consumers at a significant markup to pay for what Angley calls “bundled services.”
“A bundled service means the clinic is rolling into the total price the cost of their time, expertise, operating expenses, etc. The issue with this approach is it is not transparent and leads to the perception that the device itself costs thousands of dollars, when in reality, a portion is the device and a portion is the services,” Angley says.
The price discrepancies boil down to available features (such as Bluetooth streaming), programming features available to the audiologist, and sound processing technology. For example, hearing aids with specialized microphones called beamformers can decrease sound sensitivity in one direction while increasing sensitivity in another, which helps people more clearly understand face-to-face conversations in a noisy environment. A hearing aid with this technology costs more than one without it.
Insurance and Medicare coverage
There’s no federal law requiring insurance companies to cover the cost of hearing aids, but some state laws guarantee hearing aid coverage through private insurance, Medicaid, or the Affordable Care Act. To learn more about hearing aid insurance coverage laws by state, read our OTC hearing aid buying guide.
Some health insurance policies cover hearing aids even when it isn’t required by law. Check for hearing aid coverage in your Explanation of Benefits document or contact your provider.
The same is true for Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage) plans—some cover hearing aids and some don’t, so contact your provider for more information. Hearing aids aren’t covered through Medicare Part A or Medicare Part B.
What factors affect hearing aid prices most?
You may need to skip the following features if you want to keep OTC hearing aid costs low.
Rechargeable batteries
Hearing aids with rechargeable batteries cost more than the same model with disposable batteries. If you’re looking for an easy way to save $150 or more, select the disposable option. It costs about $30 per year to power a hearing aid with disposable batteries, which is a significant savings compared to buying a rechargeable hearing aid. That said, you’ll have to switch the batteries every three days or so, and they can be difficult to handle if you have poor dexterity or low vision.
Bluetooth streaming
The cheapest hearing aids don’t usually offer Bluetooth streaming. This technology allows you to hear audio from Bluetooth-enabled devices, like your phone, directly in your hearing aids. This improves sound quality by eliminating background noise and also lets you listen to music or a TV show without disturbing other people in the room.
The most affordable hearing aid we’ve found with Bluetooth streaming is the $500 Go Ultra from Go Hearing.
Note that Bluetooth connectivity isn’t the same as Bluetooth streaming. Hearing aids connect to apps using Bluetooth technology, but Bluetooth streaming is a separate function.
App connectivity
Apps are expensive to develop, and that price gets passed on to you when you buy an app-compatible hearing aid.
Hearing aid apps let you fine-tune settings like volume, tone, and direction. In some cases, you can also create custom presets on the app, allowing you to save settings that work well in specific environments and quickly apply them later. For example, you might use different settings in a restaurant than you would at home.
Hearing aids that don’t connect to an app may provide some presets, but they’re rarely customizable. To change settings and volume, you use buttons or dials on the hearing aid. Some respond to taps as well.
Advanced technology
Some hearing aid companies conduct industry-leading research and development. They usually sell the priciest hearing aids in an effort to recoup their investment. Examples include Neuro Sound Technology, developed by Starkey, and BrainHearing™ and RealSound Technology™, developed by Oticon. Hearing aids with these technologies use artificial intelligence to analyze incoming sounds, such as speech, and optimize the hearing aid settings for clear audio.
Affordable hearing aids lack this technology, so the audio is more likely to include distracting background noises, whistling, and static feedback. That doesn’t mean affordable hearing aids aren’t helpful—just that you’ll hear a difference between the audio of $100 and $7,000 hearing aids.
Technology also differs among affordable hearing aids with similar prices. Something as simple as directional microphones can make it much easier to hear a one-on-one conversation in a noisy environment by focusing on the sounds in front of you. The cheapest hearing aids only have one microphone that processes sounds from all directions at the same time, leading to busier audio in some environments. Examples of affordable hearing aids with directional microphones include the Jabra Enhance Plus and the MDHearing Volt and Volt Max.
Custom programming
Some hearing aids can be programmed to match your hearing test, giving you optimal sound quality. When available, this can be done remotely or in person. For example, the OTC hearing aid brand Audicus can add a tinnitus management program to your hearing aids before shipping. This level of customization is usually associated with more expensive hearing aids due to the technology and expertise required.
Quality customer support
Some OTC hearing aid companies go above and beyond for their customers by employing audiologists to answer questions and assist with programming. The cost of hiring these experts may be reflected in the price of the hearing aid. MDHearing sells the most affordable hearing aids ($299–$699) backed by free audiology support.
Affordable hearing aid companies may not invest as much money in their customer support teams, leading to generic answers and long wait times. In our experience, some of the cheapest hearing aid brands like Audien don’t even answer the phone consistently. If accessible, knowledgeable, and friendly customer care matters to you, it may be worth spending a little extra to get hearing aids from a supportive brand like the ones we recommend.
How to save money on hearing aids
Choosing an inexpensive hearing aid is the best way to keep costs low, but there are a few ways to get a discount or lower out-of-pocket expenses:
- Skip pricey features.
- Wait for sales.
- Use funds from a health savings account (HSA) or flexible spending account (FSA).
- Mention your AARP membership ID when shopping at UnitedHealthcare Hearing to get 20 percent off hearing aids and 15 percent off accessories.
- Mention your Lion’s Club ID when shopping at Beltone for 15 percent off hearing aids, plus other benefits.
Some hearing aid brands and retailers offer financing, but consider this route with caution. We’ve seen interest rates as high as 36 percent, which means you’ll end up paying significantly more in the long run despite a lower initial cost.
If you’re interested in prescription hearing aids, which are more likely to treat severe hearing loss and have a higher price tag, try Yes Hearing. This platform offers up to 40 percent off the retail price of popular prescription hearing aid brands like Oticon, Starkey, Phonak, Widex, Resound, and Signia.
You can also ask your audiologist if it’s possible to buy a prescription hearing aid without additional services bundled in.
I would encourage people to ask their providers what the service costs and what the device costs so they can more clearly understand what they are paying for.
Gina Angley, an audiologist and owner of the Tennessee-based Nashville's Hearing & Communication Center
How to get free hearing aids
Reach out to any of these organizations for more information about discounted or free hearing aids:
- Veterans Affairs.
- Hearing Aid Project.
- Hearing Loss Association of America.
- Help America Hear.
- Your local hearing aid bank, such as the Western Washington University Hearing Aid Bank Program.
- Your state’s vocational rehabilitation agency.
- Your local area agency on aging.
Top features to look for in affordable hearing aids
You may decide to skip Bluetooth streaming or artificial intelligence technology to save some money on hearing aids, but other features are non-negotiable. Look for these six features to get your money’s worth when shopping for affordable hearing aids.
Trial period or money-back guarantee
Choose a hearing aid company with at least a 45-day trial period or money-back guarantee. You need at least that much time to get used to the hearing aids and decide if they’re right for you, according to hearing experts we’ve consulted.
Did you know?
Jabra Enhance offers the longest trial period in the industry at 100 days, but this only applies to the more expensive Jabra Enhance Select 50, Select 100, and Select 200. The brand’s most affordable hearing aid, Jabra Enhance Plus, has a standard 45-day trial period like most of its competitors.
Free warranty
A warranty protects your investment from manufacturer’s defects, allowing the device to be repaired or replaced at no cost to you. A free one-year warranty is common among affordable hearing aid brands. Paying for an extended warranty may be an option with some brands, but that’s an added expense you’ll need to budget for.
Accessible and knowledgeable customer service
The best affordable hearing aid brands hire audiologists or licensed hearing instrument specialists to support their customers. Look for brands that offer onboarding calls, video conferencing, and email or live chat. Make sure there’s a way for you to get help on weekends too.
From our tester
“Inside the Go Ultra box, there’s a large ‘Need assistance?’ card with all of the contact info for customer service. Their phone line is open seven days a week from 9 a.m. to 8 p.m. EST, so you can get help on weekends and evenings. We don’t usually see that level of accessibility among affordable hearing aid brands.”
Convenient adjustments
It should be easy to adjust the hearing aids’ volume and programs so you feel comfortable wearing them. Look out for anything that could cause you to become frustrated, like screws that control volume or hearing aids that don’t change volume at the same time.
Some people prefer to control their hearing aids through a smartphone app, but this isn’t an option with some of the cheapest hearing aids like all three Go Hearing models, the MDHearing Neo, Air, and Volt, and all Audien hearing aids. Hearing aid apps become more common around the price point of $700.
Battery life and quick charge
If you choose hearing aids with a rechargeable battery, make sure the maximum battery life matches your daily schedule. Lower-cost hearing aids tend to last 12–24 hours on a single charge, but Bluetooth streaming will significantly reduce that time. If you plan to use Bluetooth a lot or travel frequently, look for a hearing aid with a portable quick-charge case. The cases can usually recharge hearing aids three times before needing to be recharged themselves. It’s a good rule of thumb to charge your hearing aids every night.
Reputable brand
There are tons of hearing aids for sale on sites like Amazon, but not all of them are backed by reputable brands. Many of them aren’t even hearing aids but are personal sound amplification products (PSAPs), which aren’t FDA-regulated and are meant to be used recreationally, such as to improve hearing while hunting.
Some cheap Amazon hearing products also make false statements, such as claiming to treat severe hearing loss. The FDA approves the sale of OTC hearing aids for treating mild to moderate hearing loss only.
If the brand doesn’t have its own website, you’re unlikely to get quality customer support, and the devices may be lower-quality. The hearing aids we recommend come from reputable brands and passed our testing protocols, so you can trust the devices in our reviews.
Where to shop for affordable hearing aids
Our recommended affordable hearing aids are easiest to buy online directly from the brand or from online retailers, like:
- Amazon.
- Best Buy.
- Walmart.
- Costco.
- CVS.
- FSA Store.
- Walgreens.
- Walmart.
Visiting your local Best Buy is the easiest way to see affordable hearing aids from Lexie Hearing, Go Hearing, and Jabra Enhance in person, but stock may vary by location. The other retailers listed above don’t typically carry hearing aids at their brick-and-mortar locations.
Our final verdict
Based on hand-testing more than 30 hearing aids, the Handbook Team recommends Jabra Enhance as the best affordable hearing aid on the market, followed by Lexie Hearing, MDHearing, and Go Hearing.
If you want a lower-cost hearing aid that actually works, expect to spend at least $300. Although you can certainly find hearing aids for less, we weren’t impressed by any of the ultra-cheap options we tested.
Paying a little extra for convenient volume controls, rechargeable batteries, good sound quality, and a comfortable fit is worth it in the long run if it means you’ll wear the hearing aids more often. With consistent hearing aid use, you’ll be more likely to experience the mental and physical health benefits of improved hearing.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, inexpensive hearing aids really do work. That said, our testers often encounter quality issues once hearing aid prices fall below $300 per pair. We recommend buying hearing aids from a company with a 45-day trial period, so you have plenty of time to get used to them before making a final decision.
We think Jabra Enhance hearing aids are the best affordable hearing aids in the market thanks to outstanding testing performance and a $799–$1,995 price range. Other affordable hearing aids we like include Lexie Hearing, MDHearing, and Go Hearing.
Medicare Parts A & B do not pay for hearing aids. If you have a Medicare Part C (Advantage) plan, look for hearing aid coverage in the Summary of Benefits document or contact your provider to see if you’re covered.
Hearing aids cost a little over $3,000 on average. OTC hearing aids are more affordable, averaging $1,600 per pair. Prescription hearing aids, which can top $7,000, cost an average of $4,600.
- Depression and hearing loss. American Academy of Audiology. (2022, May 27). Link
- Desmon, Stephanie. (21, July 2023). Hearing aids may slow dementia onset. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Link
- Donahue, A., Dubno, J. R., & Beck, L. (2010). Guest editorial: Accessible and affordable hearing health care for adults with mild to moderate hearing loss. Ear and Hearing, 31(1), 2–6. Link
- Grundfast, K. M., & Liu, S. W. (2017). What otolaryngologists need to know about hearing aids. JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery, 143(2), 109. Link
- Hearing Aids. (n.d.). Medicare.gov. Link
- State Insurance Mandates for Hearing Aids. (n.d.). American Speech-Language Hearing Association. Link